High or Low What Your Alkaline Phosphatase Levels Mean for You
What is an Alkaline Phosphatase Test?
An alkaline phosphatase (ALP) test measures the level of ALP in your blood. ALP is an enzyme that exists in many tissues throughout your body. Each tissue produces a specific type of ALP. The majority of ALP is found in your liver, bones, kidneys, and digestive system.
Abnormal ALP levels in your blood can indicate various health issues, including liver disease, bone disorders, and chronic kidney disease. However, an ALP test alone cannot determine the exact source of the ALP, so additional tests are typically required for an accurate diagnosis.
Other names for this test include: ALP, ALK, PHOS, AlKP, and ALK PHOS.
What is it used for?
An alkaline phosphatase test is primarily used to screen for or help diagnose liver or bone diseases. It can also be used to diagnose or monitor other health conditions.
Why do I need an alkaline phosphatase test?
Your healthcare provider might order an ALP test as part of a routine checkup. Many conditions can affect ALP levels, so it is often performed alongside other blood tests, such as a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP) or liver function tests, to assess liver health.
An ALP test may also be ordered if you exhibit symptoms of liver damage or a bone disorder.
Symptoms of liver disease include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Swelling or pain in the abdomen
- Swelling in the ankles and legs
- Dark urine and/or light-colored stool
- Frequent itching
Symptoms of bone disorders include:
- Bone pain
- Joint inflammation and arthritis
- Abnormally shaped or oversized bones
- Frequent bone fractures
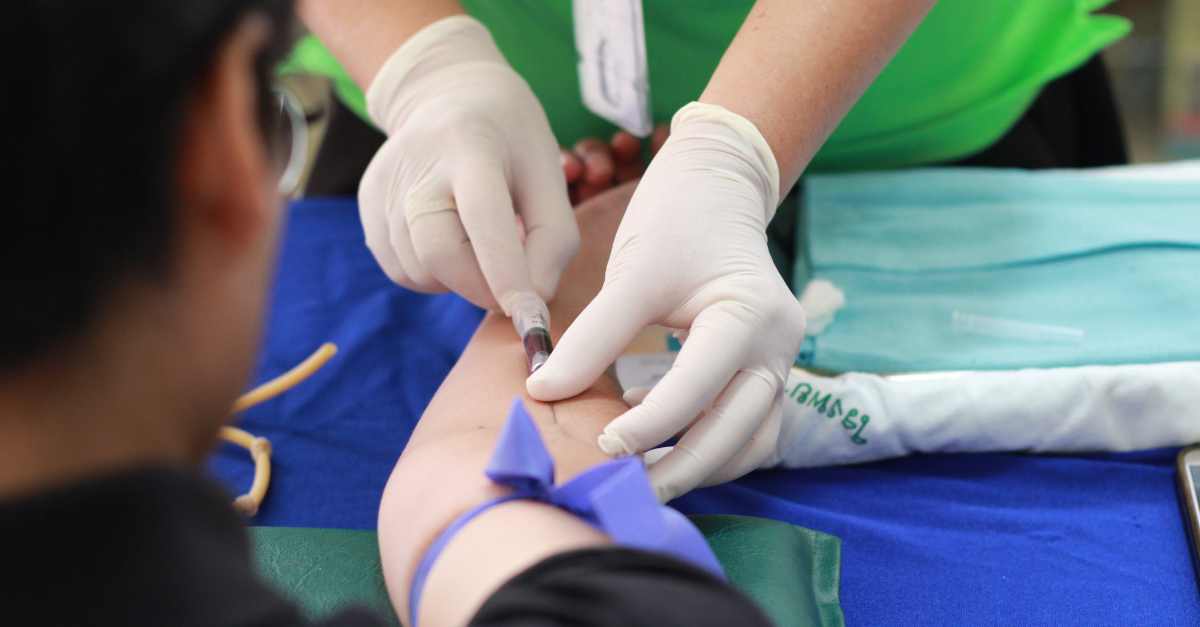
What happens during an alkaline phosphatase test?
An ALP test is a simple blood test. A medical professional will use a small needle to take a blood sample from a vein in your arm. Once the needle is in place, a small quantity of blood will be drawn into a test tube or vial. You may experience a slight sting when the needle goes in or comes out. The entire procedure typically takes under five minutes.
Should I Take Any Steps to Get Ready for the Test?
Preparation for an ALP test depends on the lab conducting the test. Some labs may require you to fast (not eat or drink) for 6 to 12 hours before the test. Since ALP tests are often done with other blood tests that may require fasting, your provider will inform you of any specific instructions.
Are there any risks to the test?
Blood tests carry minimal risk. You might experience slight pain or bruising where the needle was inserted, but these symptoms usually resolve quickly.
What do the results mean?
High ALP levels can indicate a liver problem or bone disorder. Liver issues and bone disorders produce different types of ALP, but test results alone cannot specify which type is elevated.
If your ALP levels are high, your healthcare provider might order additional tests to determine the cause. These tests may include:
ALP Isoenzyme Test: Identifies the specific source of ALP, though not widely available.
Liver Function Tests: High results suggest a liver issue.
High ALP levels from the liver may indicate:
- Bile duct blockages
- Cirrhosis
- Hepatitis
- Mononucleosis (which can cause liver swelling)
If ALP levels are high but liver tests are normal, the issue may be a bone disorder, such as Paget's disease, which causes bones to become unusually large and weak.
Moderately high ALP levels might suggest various conditions, including Hodgkin lymphoma, heart failure, or certain infections.
It is possible to have elevated ALP levels without needing treatment. Your provider will consider your symptoms, medical history, and other test results for a diagnosis.
Low ALP levels are rare but may indicate a zinc deficiency, malnutrition, pernicious anemia, thyroid disease, Wilson disease, or hypophosphatasia (a rare genetic disorder affecting bones and teeth).
Is there anything else I need to know about the alkaline phosphatase test?
Many factors can influence ALP levels. Pregnancy can increase ALP levels. Children and teenagers may have higher ALP levels due to bone growth. Birth control pills and certain medications can lower ALP levels, while other medications can increase them. Even consuming a fatty meal before the test can slightly elevate ALP levels.
For a clear understanding of your results, discuss them with your healthcare provider.
Related Blogs
-
PSA Test (पीएसए टेस्ट) - What Is It, Cost, Symptoms, And How Does It Work?
 - What Is It, Cost, Symptoms, And How Does It Work.jpg)
-
How to Lower Thyroid Antibodies Naturally and Manage Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies?

-
RDW (Red Cell Distribution Width) Test: Understanding It's Significance And Interpretation
-
Marvel Path Lab - Your Trusted Partner in Comprehensive Blood Testing

-
थायराइड क्या है? थायराइड के कारण, लक्षण और प्रभावी घरेलू उपचार (Home Remedies For Thyroid in Hindi)
.jpg)
-
Discover the Ultimate Liver Detox: Top 15 Foods to Naturally Cleanse Your Liver

-
The Ultimate Guide to Understanding MCV in Blood Tests
-
AMH Levels Unveiled: What is a Good AMH Level to Get Pregnant
-
Weil Felix Test - Marvel Path Lab

-
Exploring Fructosamine Testing: Marvel Path lab

-
Exploring Malaria Causes, Symptoms, And Cutting-Edge Diagnosis Techniques
-
Unlocking the Secrets of Fertility: Understanding Semen Analysis

-
Hot Weather, Cool Tips: Mastering Summer Wellness Like a Pro!

-
Homocysteine Test in Hindi:होमोसिस्टीन टेस्ट क्या है, खर्च, नॉर्मल रेंज, कैसे क्यों और कब होता है!

-
Optimizing Your Health Through Food Intolerance Testing: A Step-by-Step Guide

-
Your Allergy Questions Answered: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
-
Boost Your Heart Health: Simple Ways to Manage Homocysteine Levels Through Diet

-
Does MCV (Mean Corpuscular Volume) Fluctuate

-
Understanding Normal Values in a Peripheral Smear Test
-
Understanding the Prolactin Blood Test: Purpose, Procedure, and Interpretation

-
CA सीए 125 टेस्ट - क्यों किया जाता है, इसकी आवश्यकता क्या है, और जानें इसके बारे में
-
Understanding the Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) Test: A Simple Guide
 Test.jpg)
-
The MPV Blood Test Explained: What It Reveals About Your Health
-
Understanding Pancreas Blood Tests
-
Understanding the CO2 Blood Test: A Simple Guide to Your Health

-
Albumin Blood Test

-
Everything You Need to Know About the Globulin Blood Test
-
Allergy Blood Test
-
Understanding Cardiac Blood Tests: A Guide to Heart Health
-
Decoding Your Chloride Blood Test: What You Need to Know

-
Calcium Blood Tests: A Vital Tool for Assessing Bone and Heart Health
-
The Silent Indicator: Understanding the Fecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT)
-
All About the C3 Complement Blood Test: Normal, High, and Low Ranges Explained
-
Simplifying the Anion Gap Blood Test: What You Need to Know

-
CA-125 Blood Test
-
Understanding Lung Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention

-
Exploring the Long-Term Health Effects of Tobacco Use

-
Beating the Heat: Essential Tips for Staying Cool and Safe

-
Summer Health Tips: Stay Cool, Stay Healthy!

-
मंटौक्स परीक्षण (Mantoux test) के लिए व्यापक गाइड: प्रक्रिया, व्याख्या और महत्व

-
The Comprehensive Guide to ALT Blood Test

-
AST Blood Test: Your Guide to Liver Health Assessment
-
SGPT Blood Test
-
Serum Bilirubin Test in Hindi -सीरम बिलीरुबिन टेस्ट की पूरी जानकारी

-
Everything You Need to Know About the MCH Blood Test
-
Best Home Remedies to Naturally Detox Liver

-
Unveiling the Side Effects of Excessive Vitamin B12 Intake

-
Best Foods for Kidney Detox Naturally Boost Your Renal Health
-
LKM Antibody Test: A Comprehensive Guide

-
लीवर फंक्शन टेस्ट: समझें, क्या होता है और कैसे काम करता है

-
Amylase Blood Tests

-
Vanillylmandelic Acid-VMA Urine Tests
-
Everything You Need to Know About the CRP Test

-
Simple Strategies for a Healthy Liver: Your Ultimate Guide
-
Ferritin Test in Hindi (सीरम फेरिटिन टेस्ट)
.jpg)
-
Karyotyping Test Explained in Hindi: कैरियोटाइपिंग टेस्ट

-
All About PRL Blood Test and Its Impact on Prolactin Levels

-
Acid-Fast Bacillus (AFB) Tests Demystified
 Tests Demystified.jpg)
-
Acetaminophen Level Tests
-
Empowering Awareness: Your Guide to ADHD Screening

-
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Test
 Test.jpg)
-
Are You Drinking Too Much The Essential Guide to Alcohol Use Screening Tests

-
Breaking: New Study Reveals Surprising Link Between Aldosterone Levels and Heart Health

-
Attention: Must-Know Facts About Allergy Blood Testing

-
Allergy Skin Tests

-
The Role of the ANA Test in Diagnosing and Treating Autoimmune Conditions

-
The Acid Phosphatase Test: What You Need to Know About Sample Types and Report Timing

-
Albumin Fluid Test: Significance, Sample Types, and Report Timeline

-
Ammonia Blood Test: Sample Type, Report Generation Time, and Diagnostic Importance
-
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE): Its Role, Sample Types, and Report Generation Time
 Its Role, Sample Types, and Report Generation Time.jpg)
-
Bile Acid Total Blood Test: Sample Type and Report Generation Time Explained
-
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) Levels Explained: Fast, Accurate Testing with Blood Samples at Marvel Path Lab
 Levels Explained Fast, Accurate Testing with Blood Samples at Marvel Path Lab.jpg)
-
Amniocentesis Fluid Test : the Procedure, Sample Type, and Report Results

-
The Hidden Dangers of Bird Flu: What You Need to Know About Avian Influenza

-
Zika Virus : ज़ीका वायरस के कारण , लक्षण और बचने के उपाय

-
तेजी से फ़ैल रहा है West Nile Virus जाने यह बीमारी क्या है और इससे कैसे करे अपना बचाव
 48 मामलो की हुई पुष्टि.jpg)
-
25 की उम्र पर करते ही हर पुरुष को ये 10 टेस्ट जरूर करवाने चाहिए

-
25 की उम्र पार करते ही महिलाओं को ये 7 टेस्ट करवाना क्यों है जरूरी

-
हर शादीशुदा महिला के लिए जरूरी 10 टेस्ट: सेहतमंद रहने के लिए आज ही करवाएं!

-
इन 10 खाद्य पदार्थों को डाइट से गायब न करें वरना थायरॉयड की समस्या बढ़ सकती है!

-
अगर आपको भी डेंगू है, तो हो जाएं सावधान – आज ही करें ये घरेलू उपचार

-
अगर आपको भी दिख रहे हैं ये लक्षण तो हो जाएं सावधान, आपका लिवर सड़ चुका है तुरंत करवाए लिवर टेस्ट

-
प्लेटलेट्स बढ़ाने के लिए 6 अचूक उपाय – आज ही शुरू करें!
.jpg)
-
हर महिला को यह 5 ब्लड टेस्ट जरूर करवाने चाहिए – जानिए क्यों!

-
विटामिन की कमी का पता लगाने और सुधारने के लिए ब्लड टेस्ट का सही तरीका

-
7 Warning Signs of Dengue Fever in Hindi : जानें कैसे पहचानें और खुद को बचाएं!

-
डेंगू में प्लेटलेट्स कैसे बढ़ाएं: घर बैठे अपनाएं ये 10 चमत्कारी घरेलू उपाय, रिजल्ट चौंका देंगे!

-
Rashes In Dengue Is Good Or Bad डेंगू में रैशेज: क्या ये आपकी सेहत के लिए अच्छे हैं या खतरनाक संकेत जानिए सच्चाई!

-
Dengue Antibody Igm Positive Means :क्या होता है जब डेंगू एंटीबॉडी IgM पॉजिटिव आए यहाँ जानें!

-
अगर आपको ये 7 लक्षण दिखें, तो हो सकता है टाइफाइड! तुरंत जानें टाइफाइड के लक्षण और बचाव के उपाय

-
Dengue Symptoms In Babies : बच्चों में 7 चौंकाने वाले लक्षण जो हर माता-पिता को जानने चाहिए!

-
How Many Days To Recover From Dengue : जल्दी ठीक होने के लिए अपनाएं ये 6 टिप्स!

-
Monkeypox Symptoms मंकीपॉक्स के 7 खतरनाक लक्षण: जानें कैसे बचें और सुरक्षित रहें!
-
Viral Fever Treatment At Home : वायरल बुखार से छुटकारा पाने के 8सरल घरेलू उपाय जानें कैसे करें इलाज

-
What To Eat During Fever : बुखार में क्या खाना चाहिए जानिए 7 सुपरफूड्स जो तेजी से ठीक करेंगे!

-
इन 15 खाद्य पदार्थों को न छोड़ें वरना आपका लिवर कभी भी साफ नहीं रहेगा

-
Rashes After Fever In Adults: क्या बुखार के बाद रैशेस सामान्य हैं जानें लक्षण, कारण और उपाय!

-
Scarlet Fever Symptoms : आपके बच्चे को हो सकता है स्कार्लेट फीवर! लक्षण और इलाज की पूरी जानकारी

-
थायरॉयड के इन लक्षणों को न करें नजर अंदाज: तुरंत कराएं जांच जानें थायरॉयड बीमारियों का सरल इलाज

-
What Health Problems Are Associated With Low Blood Pressure : जानें कैसे पहचानें और बचें गंभीर समस्याओं से

-
4 Stages Of Typhoid Fever : जानें पहचानें और तुरंत इलाज करें!

-
Test For Dengue Fever : जानें पूरी जानकारी और सही समय पर टेस्ट करवाएं

-
Viral Fever Duration In Child : क्या आपका बच्चा वायरल बुखार से जूझ रहा है जानें इसके लक्षण और उपचार!

-
बस ये 5 चीजें खाएं और 1 हफ्ते में विटामिन B12 की कमी करें दूर, जानें आसान तरीके!

-
यूरिक एसिड को कंट्रोल करने का जादुई तरीका – सिर्फ ये चीज़ खाएं और पाएं राहत!

-
बस रात को खाएं ये एक चीज़ और देखें कैसे बढ़ता है विटामिन D!

-
क्या आप जानते हैं दुनिया में कितने प्रकार के ब्लड ग्रुप होते हैं यहां जानिए सब कुछ!

-
Which Path Lab Is Best In India: कैसे मार्वल पैथ लैब ने बदल दी पैथोलॉजी की दुनिया जाने कैसे !

-
Can you take vitamin B12 every day : क्या आप हर दिन विटामिन बी12 ले सकते हैं जानें इसके अद्भुत फायदे और सही खुराक!

-
क्यों होते हैं बुजुर्गों को कैंसर जानें 7 चौंकाने वाले कारण!

-
नवरात्रि में ये 10 सुपरफूड्स खाएं, माता रानी होंगी प्रसन्न और आप रहेंगे फिट!

-
Blood Test For Allergy : बार-बार छींक, खुजली, या सांस की दिक्कत, ये ब्लड टेस्ट आपके सभी सवालों का जवाब देगा!

-
PTH Blood Test: अगर दिख रहे हैं ये संकेत, तुरंत करवाएं ये जरूरी टेस्ट और जानें इसका पूरा प्रोसेस!
-
यूरिक एसिड को मिनटों में कम करें जानें 10 घरेलू नुस्खे जो तुरंत असर दिखाएंगे!

-
पूरे 9 दिन भूख से रहना चाहते हैं दूर, नवरात्रि में बस यह एक चीज खाएं!

-
Ratan Tata News : रतन टाटा जी का स्वास्थ्य रहस्य कैसे उन्होंने बनाए रखा अपनी सेहत

-
Crimean Congo Hemorrhagic Fever : लक्षण, कारण और और सही समय पर टेस्ट कराने की जरूरत अवश्य पढ़ें!

-
What Is Eosinophils In Blood Test ? आसान भाषा में जानिए!

-
सर्दी-खांसी से राहत या त्वचा की चमक? जानिए कच्ची हल्दी वाला दूध के 9 जबरदस्त फायदे!

-
Breast Cancer Recurrence Blood Test: The Life-Saving Check Every Survivor Needs to Know About!

-
Dementia Blood Test: How It Helps in Early Diagnosis and What You Should Know
-
Ding Liren Mental Health Issue: The Silent Struggle of a Chess Champion

-
UIBC Blood Test: Everything You Need to Know About Iron Levels in Your Body

-
HBAC ब्लड टेस्ट: यह टेस्ट क्यों ज़रूरी है और क्या बताता है?

-
क्या विटामिन B12 खतरनाक है? पूरी सच्चाई जानें!

-
Dual Marker Blood Test : जानिए यह टेस्ट क्यों जरूरी है और इसकी पूरी जानकारी

-
लिम्फोसाइट्स (Lymphocytes ) क्या होते हैं? पूरी जानकारी आसान भाषा में!
 क्या होते हैं पूरी जानकारी आसान भाषा में!.jpg)
-
गर्मियों में खुद को हाइड्रेटेड और हेल्दी कैसे रखें? | Marvel Path Lab की एक्सपर्ट गाइड

-
फैटी लिवर पेशेंट के लिए वरदान है ये चीज – Diet Tips to Improve Liver Health






